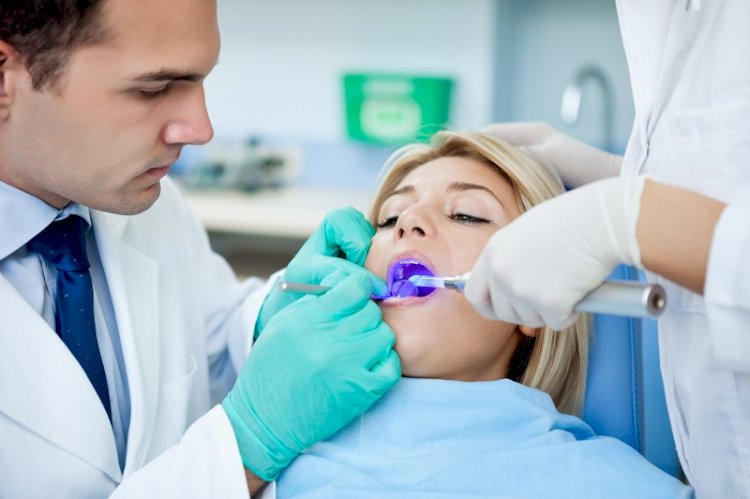
Surgical Instruments: Buying Guide
We must never forget that they are tools that require special care, as poor maintenance can cause them to deteriorate quickly. The surgical instruments can be cleaned in special ultrasonic tubs or in simple tubs for sterilization, even if the recommended sterilization method is that of steam in an autoclave. It is obvious that surgical instruments showing signs of corrosion must be eliminated immediately and replaced with new ones.
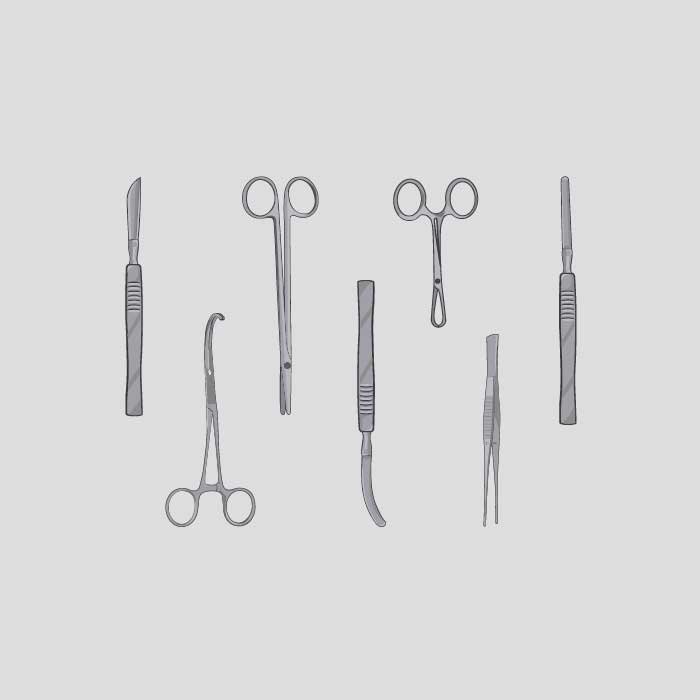
There is a wide range of surgical instruments, intended for exclusive use by specialized medical personnel. It is of primary importance to know each instrument specifically, both from a constructive and functional point of view. Understanding their use in detail in the various phases of a surgery allows the professional to be able to count on maximum functionality and reliability during the performance of their work. Only the perfect balance between these two factors can contribute to a continuous improvement of one's performance.
Surgical instruments names and description:
Nomenclature
The nomenclature of surgical instruments is structured according to certain models and the naming principle can vary based on multiple factors, for example: a description of the actions it performs (for example, scalpel, hemostat),the name of its inventor ( for example, the Klemmer forceps ),the scientific name of the organ related to the type of surgery (for example, a tracheotome is an instrument used to perform a tracheotomy).The nomenclature is very important as it makes us understand the instruments that are set up on the surgical trolley .
An excellent organization allows to maintain a real order of the instrumentation and at the same time a mental order related to the intervention in execution. Now we will analyze the different categories of instrumentation:
1. Sharp surgical instruments
All those instruments used for incision and for the section of tissues and integuments are considered as such. The main instruments in this genre are undoubtedly the scalpel and the scissors. a) Scalpels Mainly used for skin incision, they are also used to incise or dissect soft tissues, viscera or vessels. There are several, divided according to the handle, size, length and shape. The handles of multipurpose scalpels currently used in surgery belong to the Bard-Parker type, on which different numbers of blades are inserted. The blades they differ in shape and cut: they can be rounded (mainly used in skin incisions), lanceolate (used for abscessal incisions) and pointed. b) Scissors They differ in shape, length, strength and angle. Used for the dissection of tissues, vessels, viscera and the cutting of sutures and aids. The scissors are a cutting tool and may have different lengths (16, 20, 24 cm) to act at different depths. They can be straight or curved and have different types of blades, among which we find alternating, blunt or
acute. They are used to dissect robust anatomical structures and to cut sutures or other material. Given the delicacy of the blade, they must not be used for improper uses or to try to cut structures that require more specific tools (metal wires).
2. Forceps
The forceps can be classified into 4 categories: a) Dissection forceps: they are divided, in turn, into surgical forceps, anatomical forceps, vascular or atraumatic forceps and coagulation forceps. Their length can vary and are available short, medium, long and extra-long, depending on the depth of the surgery. b) Grasping forceps: these are those surgical instruments characterized by a ring handle, a rack with a distinct bite tip with indentation or knurling. Their main function is to be able to grasp and pull the tissues with atraumatic action and with little damage to the bite. c) Hemostatic forceps: characterized by a ring handle, they differ in temporary and definitive hemostasis. They can have different lengths: baby, short, medium, long, very long and are also divided into curved and straight. One of the most popular hemostatic forceps is certainly the Klemmer forceps, which is part of the Klemmer surgical instruments. Its value lies in the build quality and portability, thanks to its small size (the smallest size starts at 14 cm). d) Pliers to fix them: they are tools used to fix the multipurpose drapes in the preparation of the surgical field in the operating room. There are various types, the most common are the secure them pliers Backhaus and secure them pliers Bernhard.
3. Retractors
They are divided into retractor retractors and self- propelled retractors and of both categories there are various shapes, sizes and mechanisms. Their function is to obtain a favorable exposure of the operative field. The retractor retractors are handled by assistants of the team leader, while the self-retaining retractors autonomously maintain the set position.
4. Needle Holder
These are instruments necessary in surgery for manual needle suturing, characterized by ring handle, rack, body and bit. They have different length, weight, strength and bite size according to the abdominal depth, the viscera, the strength of the tops and the type of needle. The particular groove of the bit allows the sealing of the needle. It is usual to distinguish them into: delicate needle holders, intestinal needle holders, wall and skin needle holders. The surgical instruments that we have just analyzed, represent only a part of all those available on the market, but it appears to be a functional subdivision, in such a way as to be able to clarify this type of instrument.
We must never forget that they are tools that require special care, as poor maintenance can cause them to deteriorate quickly. The surgical instruments can be cleaned in special ultrasonic tubs or in simple tubs for sterilization, even if the recommended sterilization method is that of steam in an autoclave. It is obvious that surgical instruments showing signs of corrosion must be eliminated immediately and replaced with new ones.
Share
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0